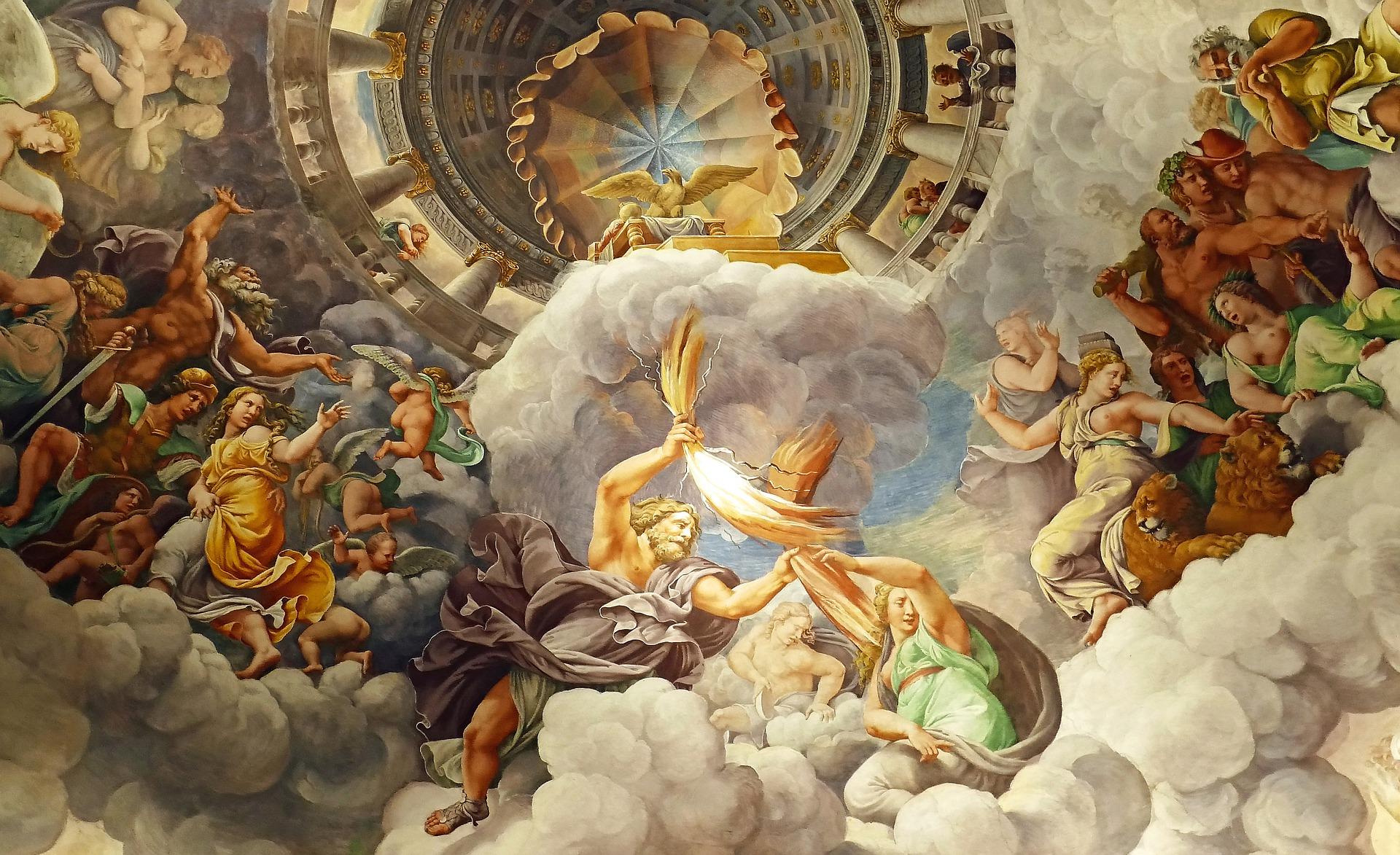
The Greek Gods is a pantheon that consists of 12 different deities that all resided on Mount Olympus. These Gods were the center of ancient Greek religion. Aside from the 12 Olympians, there are so many more Greek Gods out there as part of their ancient mythology. This article will discuss just 5 of these 12 Greek Olympians.
Zeus: King of Olympus
In the Roman language, Zeus is known as Jupiter. He is the God of the sky and the king of Olympus. His wife and sister, Hera, was the Goddess of marriages and ruled as the Queen of Olympus. Hera’s marriage to Zeus was not a happy one as Zeus continued to have affairs with other goddesses as well as nymphs and mortals. They had three children from their union together. Their children include Ares, the god of war, Hebe, a young and perpetual beauty, and Eileithyia, the goddess of childbirth.
King Zeus displayed his unhappiness by throwing thunderbolts and affecting the weather. His symbols are the oak and the thunderbolt, which were his most potent weapons. Many storytellers portray Zeus as the master of the universe. As such, he had great responsibilities. He was the lawmaker who sent down and ensured that all mortals and immortals obeyed the laws. He was the one who sent down rain to fertilize the Earth. Zeus, the king of Olympus imposed discipline and order in the universe, assigning a place to the stars and the planets. Though extremely powerful, he ruled over his kingdom wisely and justly.
Poseidon: The Greek God of the Sea
Called Neptune in Roman mythology, Poseidon is the God of the sea. His beautiful palace was underwater, and he would cause earthquakes when he became angry. Poseidon was sensitive about his subordinate position to Zeus and frequently argued about his other rights with his brother. He married Amphitrite, who was the daughter of Nereus. He was the father of three children and was very protective of them.
Many claim that Poseidon also created the horse. He rode upon his magnificent gold chariot, drawn by two beautiful white horses with gold manes.
Hades: The God of the Underworld
Hades is the god of the underworld and the king of the dead. In Roman mythology, they call him Pluto. Men both loathed and feared him. He was fiercely private, and did not welcome anyone. Those who visited the underworld were rarely allowed to leave. He preferred the darkness of his world and had ownership of all the gems and metals under the earth’s surface. A vicious watchdog with three heads guarded the gate to keep the dead within the underworld.
Hades was responsible for overseeing all the punishments that the gods handed down to the dead. Hades was grimly cold, but he was not evil. He would only supervise the punishments, as was his duty. However, Erinyes carried out the actual torture. Nobody was willing to say or take his name out of fear of incurring his wrath.
Apollo: The Greek God of Music, Healing, and Light
Apollo was the son of Zeus and Leto. He was the God of music and healing. Initially, he was a herdsman and was responsible for protecting herds and flocks. However, his talent as a musician soon turned him into the God of music. Apollo also had skills in archery and enjoyed hunting. In addition, Apollo had the power to send plagues upon mortals.
Ares: God of War
Born to Zeus and Hera, Ares was both cowardly and cruel. He was the god of war but was not a skillful warrior. He was often humiliated, defeated, and forced to run from the battlefield. Ares was unscrupulous and would switch sides even in the middle of a war. He took immense pleasure in the bloodshed and the slaughter that came with war.
Final Thoughts on Greek Gods
These are only a few of the gods that the ancient Greeks worshipped for various reasons. Western civilization has been greatly influenced by Greek mythology, with it affecting their art, culture, and literature. Scholars have studied the Greek myths to learn and shed light upon ancient Greece’s political and religious institutions.